High-Efficiency Overcurrent Protection and Monitoring for Data Centers: Highly Integrated 50A E-Fuse
High-Efficiency Overcurrent Protection and Monitoring for Data Centers: Highly Integrated 50A E-Fuse
The increasing demands of compute-intensive applications and large-scale data processing require servers and other network equipment to have a stable high-current supply to support high-performance computing. With the significant rise in power requirements, power systems must possess efficient overcurrent protection and monitoring capabilities.
Traditional high-current power protection solutions often rely on multiple discrete components. However, in high-power application scenarios, these solutions face challenges such as increased design complexity, excessive space occupation, and maintenance difficulties. To meet the demand for a smaller footprint, the number of components used is continuously decreasing. With product time-to-market shrinking, engineers need ways to simplify designs. IVS provides an innovative solution to address these design challenges.
IVS introduces the 50A highly integrated E-Fuse, IS6105A, a chip specifically designed for hot swap protection. It can effectively protect the input from output short circuits and transients. During startup, the output voltage slew rate can be set to limit inrush current. The IS6105A integrates a MOSFET and sense resistor internally and is equipped with a PMBus digital communication interface. It highly integrates power protection, monitoring, and control functions into a single silicon chip. While effectively handling high current loads, it minimizes the number of external components required, simplifying system design.

The IS6105A supports a wide input voltage range of 4V to 16V, features current monitoring (IMON), and incorporates a power MOSFET with an RDS_ON of 1.2mΩ. Its advanced on-chip current sensing technology enables fast and accurate current detection. The chip features an internal auxiliary function to discharge external output capacitor energy. When protection is triggered or the enable is turned off, it can reduce the output voltage faster, shut down the downstream circuit, achieve rapid power-down of the load circuit under abnormal conditions, and fulfill the circuit protection function.
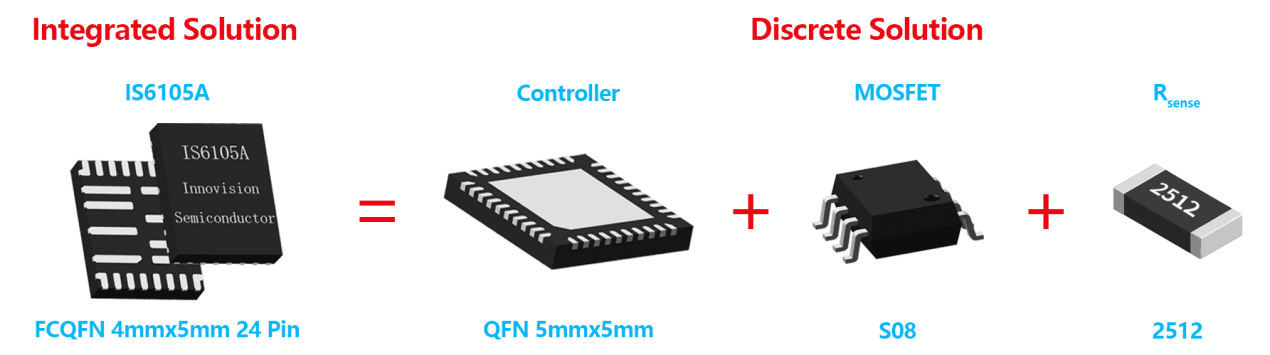
High Level of Integration
The IS6105A integrates the functionalities of many discrete components into a compact 4mm x 5mm package. The chip integrates a comprehensive control function module, a high-precision detection module, and a low-on-resistance, high-speed switching MOSFET. Compared to discrete combinations, this chip can reduce the number of peripheral components, saving design space and cost.
PMBus Protocol Communication Compatibility
The IS6105A is compatible with the PMBus 1.3 standard, providing a simple and flexible configuration method, precise system control for circuit boards, and specific monitoring and telemetry technology. The PMBus interface allows programming various parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, and fault parameters, and reading/reporting real-time information. Users can dynamically adjust these parameters to quickly and conveniently integrate power supply information for more efficient power management. This meets the multiple needs of data centers for high current, high-efficiency protection, and system simplification. As shown below, an example of modifying the OVP protection mode via PMBus for the IS6105A:
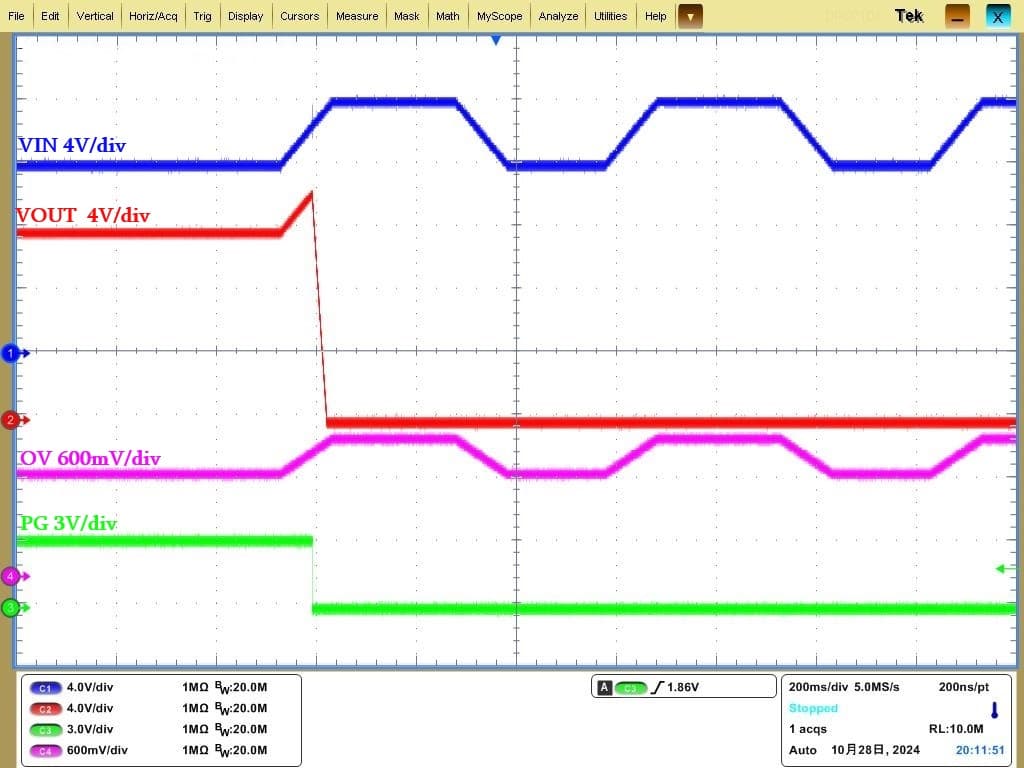
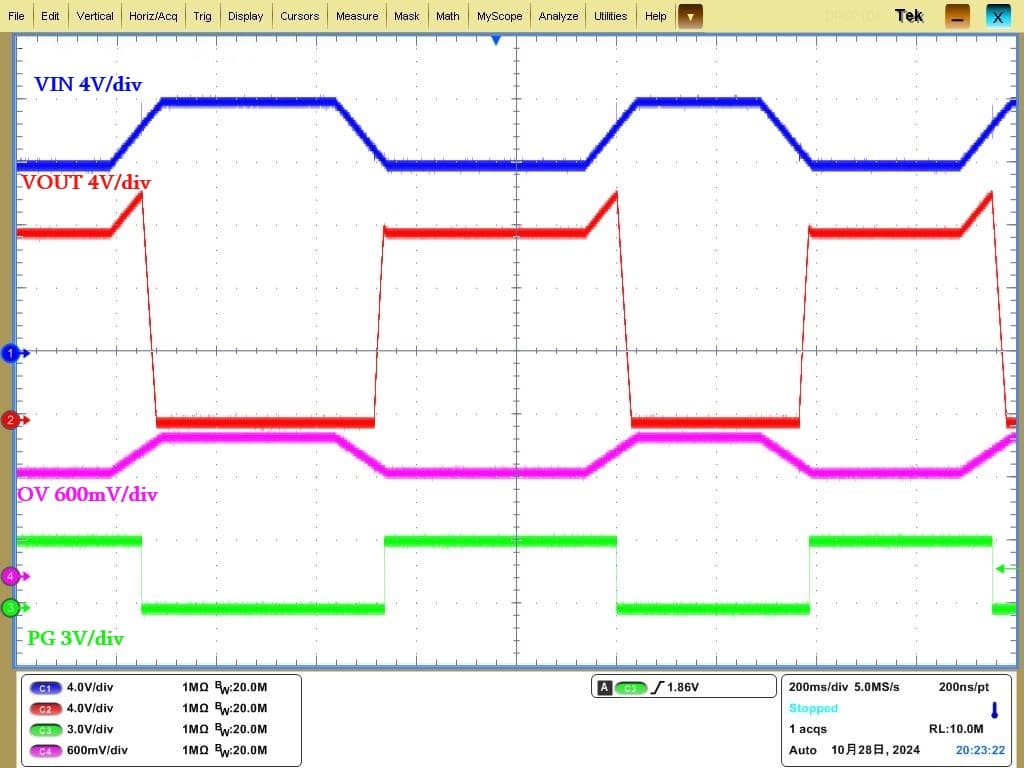
Comprehensive, High-Precision Current and Voltage Signal Acquisition
While supporting reading real-time voltage and current values via the PMBus protocol, the IS6105A utilizes internal high-precision voltage and current acquisition modules to quickly obtain and respond to data such as instantaneous voltage (VIN/VOUT), current (IOUT), temperature (Temperature), and power (PIN). For circuit applications not requiring PMBus communication, the IS6105A can generate a voltage proportional to the device current through an external resistor from the IMON pin to ground, enabling current monitoring and feedback.
Figure: VIN Accuracy within ±1% of Full Scale Range Figure: VOUT Accuracy within ±1% of Full Scale Range Figure: Temperature Accuracy within ±3% of Range Figure: PMBus IOUT Accuracy within ±5% of Full Scale Range Figure: Imon Accuracy: ±3% for 10A-50A within Full Scale Range
Support for Hot Plug Applications
As with many communication infrastructures, high availability and high reliability are key elements in data center system design. Pluggable modules and PCBs (such as servers and storage devices) require protection and control circuits at the power interface, commonly referred to as hot swap control circuits.
In hot plug applications, the input can generate extremely high voltages at the moment of insertion, posing a risk of overvoltage breakdown for downstream devices. To prevent instant high voltage from propagating to the E-Fuse's downstream side and damaging components, power-up should be avoided immediately after insertion; it's best to wait for the input voltage to stabilize. The IS6105A allows users to delay chip startup by a preset insertion delay, avoiding the jitter voltage at the insertion moment. From the moment of insertion, a timer starts counting the insertion delay. When the timer finishes counting and power-up conditions are met, VOUT begins a soft start. Introducing an insertion delay via timer counting can effectively prevent the risk of overvoltage breakdown in downstream devices due to unstable voltage at insertion.

High-Speed Fault Response
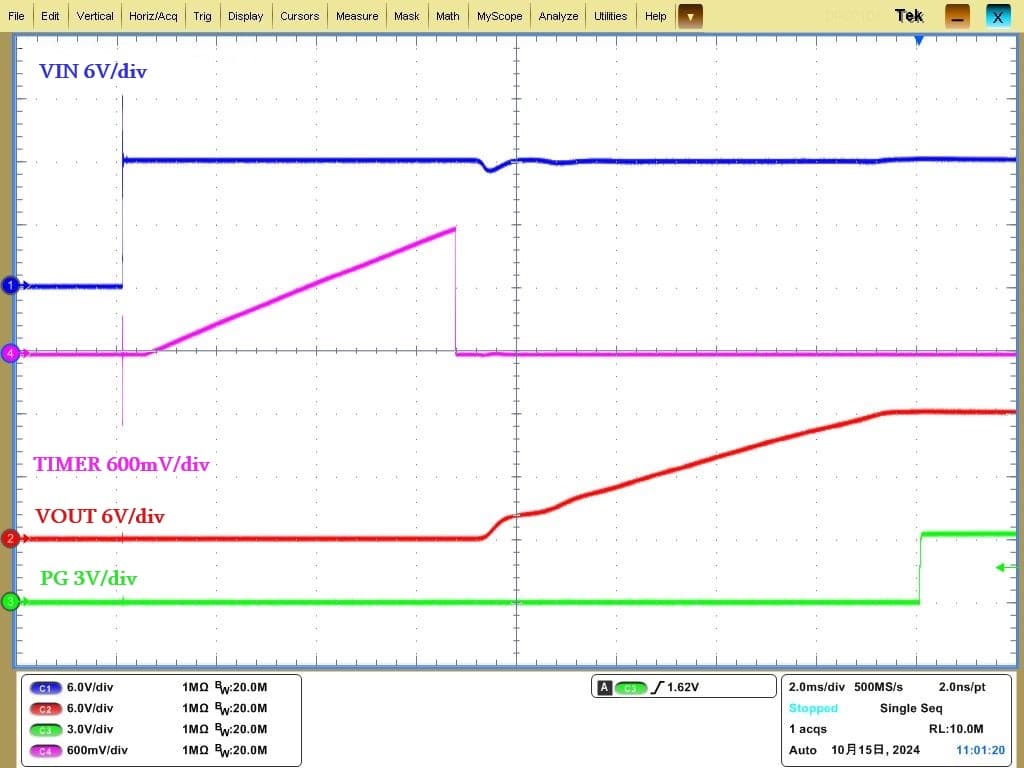
To prevent shutdowns caused by load power or device short circuits or overloads, users can set the E-Fuse's maximum current limit via the ISET pin. When a current exceeding the set value is detected, the system will limit the current and start a fault timer. If the current drops to a normal value within the timing period, the chip can promptly exit the OC state and resume operation (OC RECOVER). Conversely, if the current fails to drop below the set value after the timer expires, the chip will disable the current limiting function, pull the fault reporting pin low, and quickly cut off the circuit (OCP).
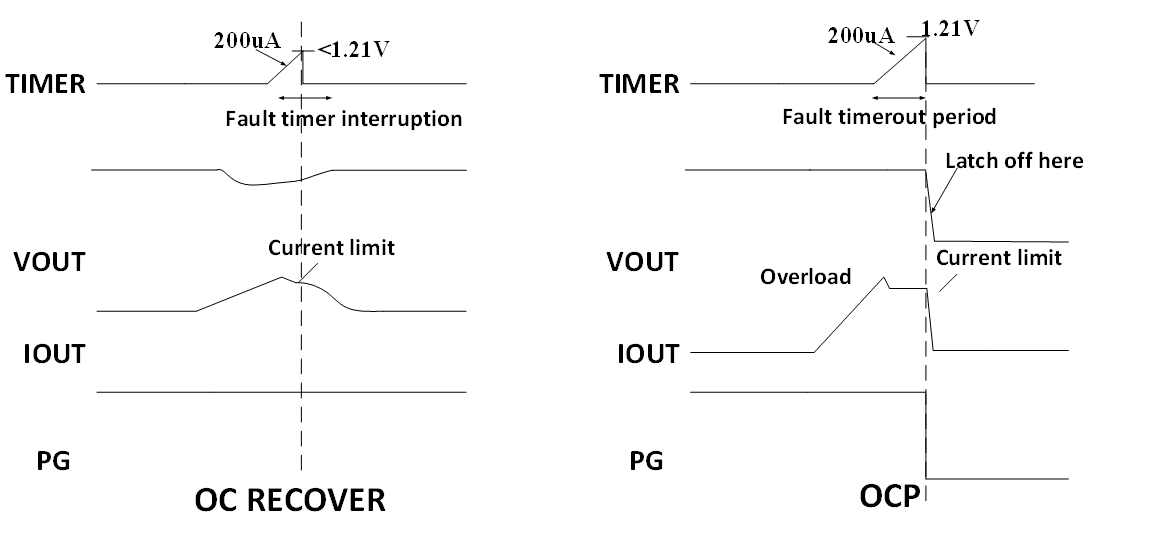
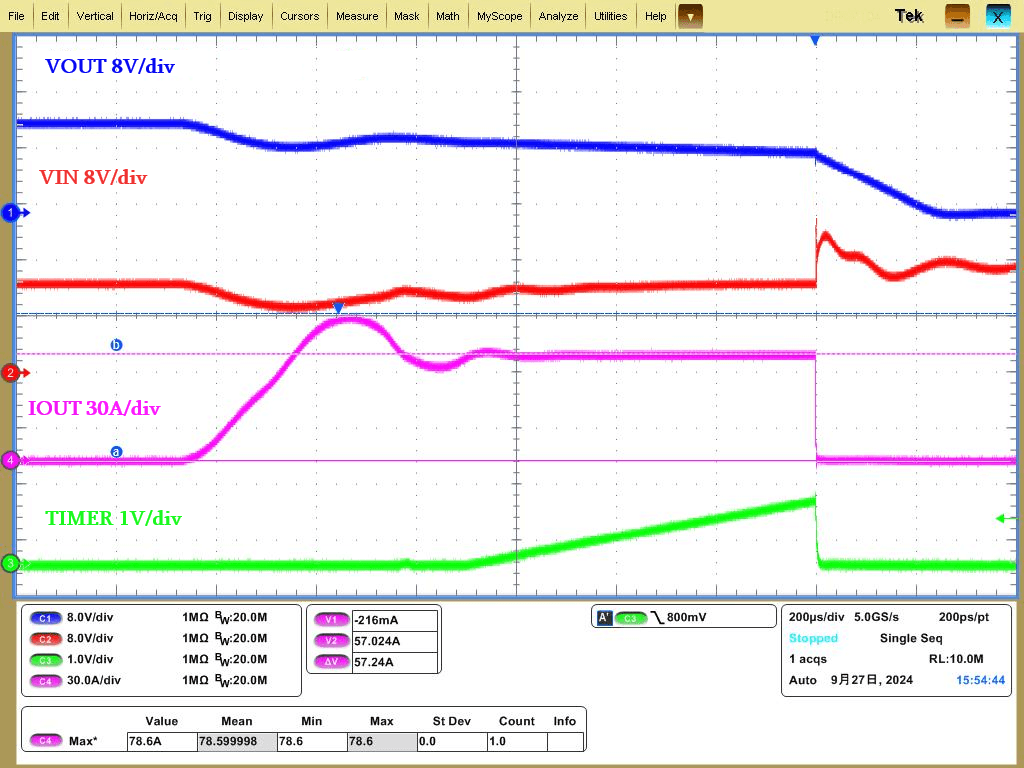
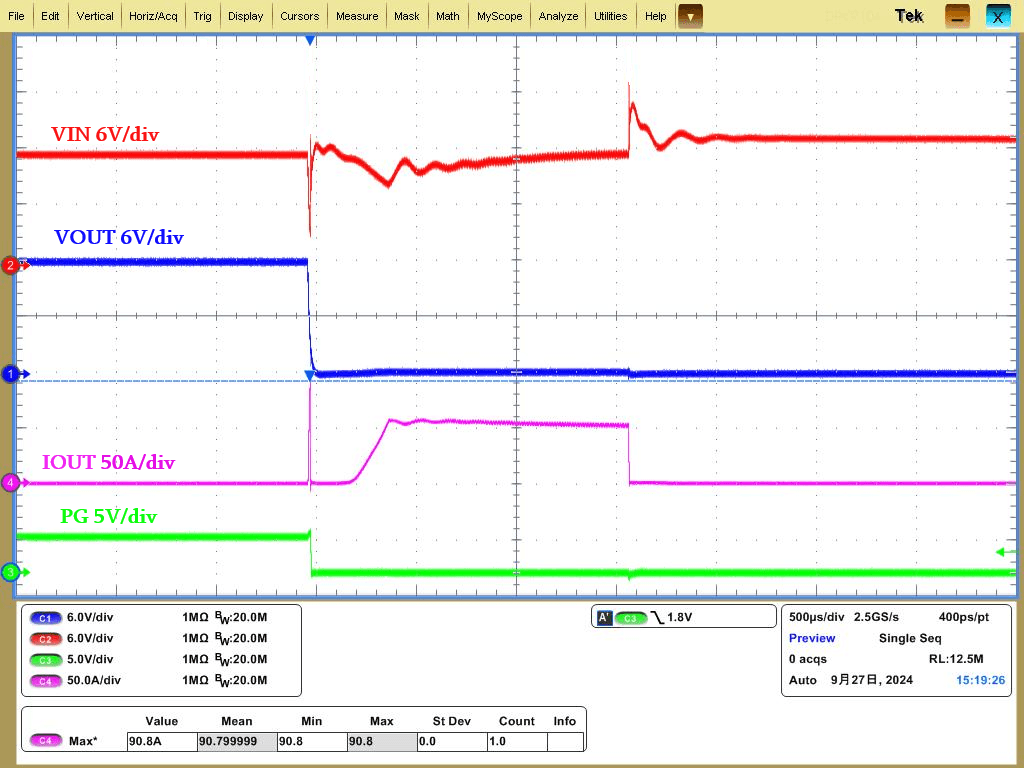
For instant high currents with faster rise times and larger values, the IS6105A will immediately trigger SCP protection, responding within 200ns and turning off the FET. After a set time interval, it attempts to self-recover with limited current power-up. If it fails to exit the overcurrent state, the chip will cease power-up attempts and enter latch mode, waiting for the user to manually restart after troubleshooting.

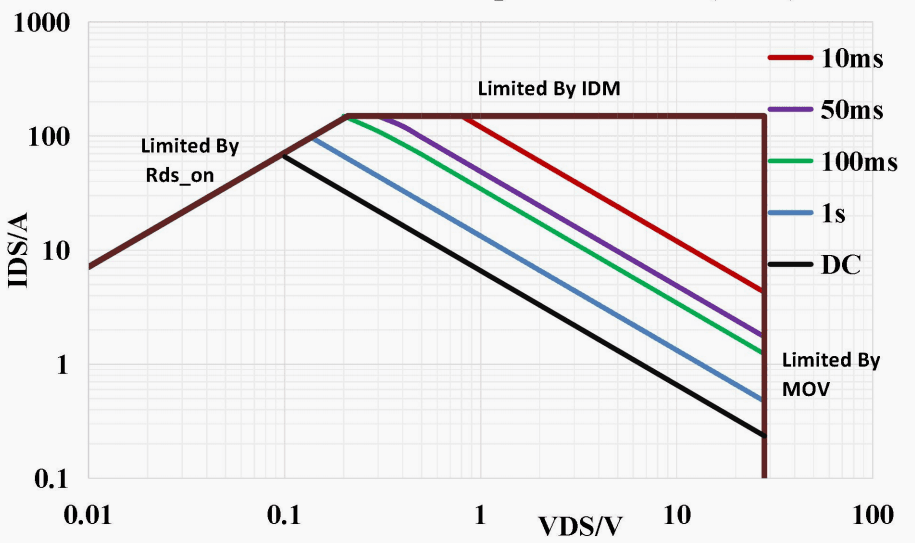
Ample Safe Operating Area (SOA)
As the MOSFET is crucial for E-Fuse operation, its Safe Operating Area (SOA) parameters determine the upper limit of the E-Fuse's electrical performance. A larger SOA means the chip can operate safely and stably over a wider voltage and current range. The figure below shows the SOA of IS6105A. It can be seen that as an E-Fuse supporting a constant 50A load, its limiting current is 110A, providing an extremely ample current margin. Even with momentary high current surges, the IS6105A can still operate normally.
To prevent the combined effect of excessive VDS and IDS before MOSFET turn-on from exceeding the SOA, the IS6105A has comprehensive preventive functions. In addition to using soft-start to suppress inrush current, the chip also implements a current limit during soft-start power-up to ensure the MOSFET operates within the SOA.